
In general, you find metals on the left-hand side of the periodic table and non-metals on the right-hand side. Notice that:
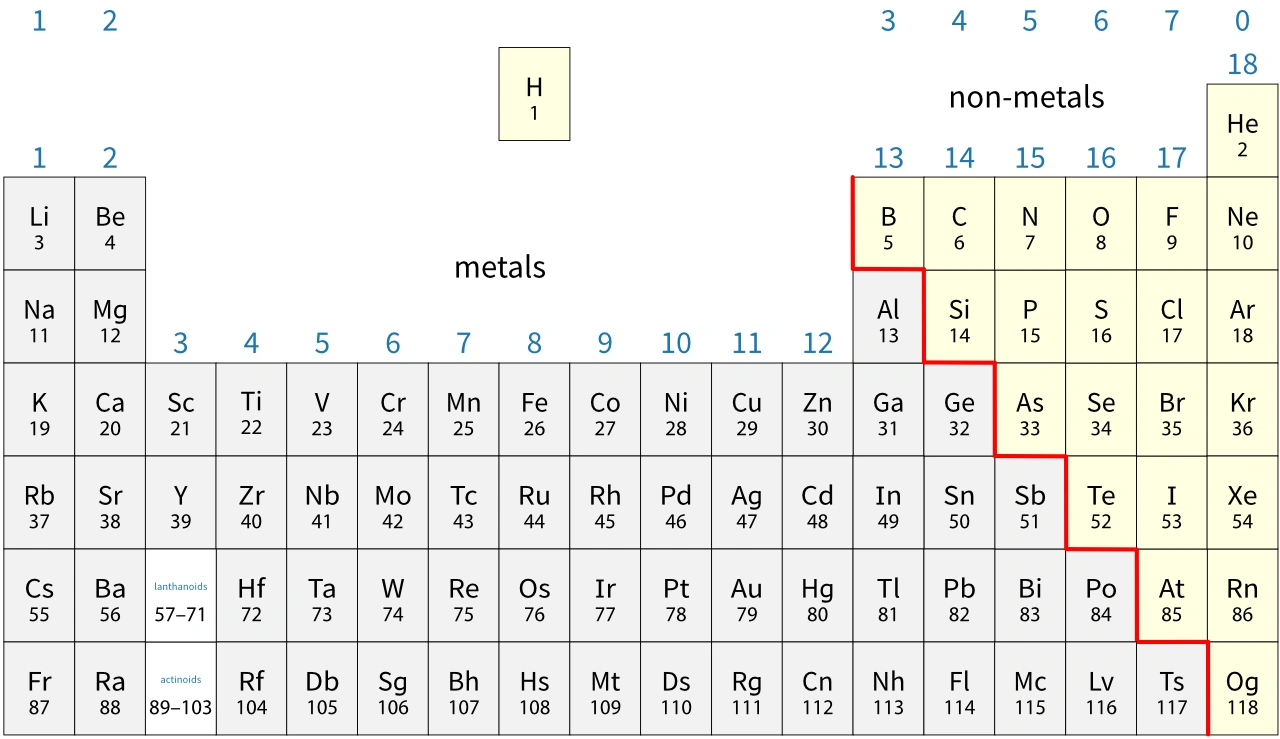
Tennessine (Ts) may be a metalloid, but very little is known about its properties.
A property is a feature of something that can be measured or observed:
The typical properties of metals and non-metals are different.
The table summarises some typical physical properties of metals and non-metals.
| Physical property | Metals | Non-metals |
|---|---|---|
| Melting point and boiling point | High | Low |
| Appearance when solid | Shiny | Dull |
| Density at rtp (room temperature and pressure) | High | Low |
| Electrical conductivity | Good | Poor |
| Thermal conductivity | Good | Poor |
| Response to external forces when solid | Malleable and ductile | Brittle |

Remember that these are typical properties. Some metals and non-metals have different properties to these. For example:
A property is a feature of something that can be measured or observed:
The typical properties of metal and non-metal elements are different.

The table summarises some typical physical properties of metals and non-metals.
| Physical property | Metals | Non-metals |
|---|---|---|
| Melting point and boiling point | High | Low |
| Appearance when solid | Shiny | Dull |
| Density at rtp (room temperature and pressure) | High | Low |
| Electrical conductivity | Good | Poor |
| Thermal conductivity | Good | Poor |
| Response to external forces when solid | Malleable and ductile | Brittle |
Remember that these are typical properties. Some metals and non-metals have different properties to these. For example:
The table summarises some typical chemical properties of metals and non-metals.
| Chemical property | Metals | Non-metals |
|---|---|---|
| Bonding between atoms | Metallic | Covalent |
| Reactions with metals | None - mixtures (alloys) form | Ionic compounds form |
| Reactions with non-metals | Ionic compounds form | Simple molecules or giant covalent structures form |
| Ions formed in reactions and during electrolysis | Positively charged (cations) | Negatively charged (anions) |
| Oxides | Basic (soluble oxides form alkaline solutions) React with acids | Acidic React with bases |
Remember that these are typical properties. Some metals and non-metals have different properties to these. For example:
Silica, SiO2, is in the solid state at room temperature. Predict three properties of this compound. Explain your answer.
Show the answerSilica is likely to have a giant covalent structure. It should have acidic properties and be able to react with bases.
This is because silica is a compound of two non-metals, silicon and oxygen. These compounds have covalent bonding, and covalent substances in the solid state usually have a giant structure. The oxides of non-metals are acidic and react with bases.

Chemical reactions involve atoms losing, gaining or sharing electrons. The more easily this happens, the more reactive an element is.
Metal atoms lose electrons when they react with non-metals. They form positively charged ions when they do this. The table summarises the link between a metal’s position in the periodic table and the ions it forms in reactions.
In general, group 1 metals are more reactive than group 2 metals, and these are more reactive than group 3 metals. Also, metals become more reactive as you go down a group. This means that the most reactive metals are found towards the bottom left of the periodic table.
… the transition elements (the large block of metals between groups 2 and 3) are relatively unreactive compared to other metals. They include:
Suggest a reason why iron, Fe, is less reactive than potassium, K. Give your answer in terms of the positions of these two metals on the periodic table.
Show the answerPotassium is in the middle of group 1, which contains very reactive metals. Iron is a transition element, and these are relatively unreactive.

Non-metal atoms gain electrons when they react with metals. They form negatively charged ions when they do this. The table summarises the link between a non-metal’s position in the periodic table and the ions it forms in reactions.
In general, group 7 non-metals are more reactive than group 6 non-metals, and these are more reactive than group 5 non-metals. Also, non-metals become more reactive as you go up a group. This means that the most reactive non-metals are found towards the top right of the periodic table.
… the atoms of elements in group 0 (group 18) have full outer shells. This means that they have no tendency to lose, gain or share electrons. Group 0 elements are very unreactive because of this.
![]()
This website uses cookies to improve your experience. I'll assume you're okay with this, but you can opt-out if you wish. Read More
Cookies are small text files that can be used by websites to make a user's experience more efficient. The law states that we can store cookies on your device if they are strictly necessary for the operation of this site. For all other types of cookies we need your permission. This site uses different types of cookies. Some cookies are placed by third party services that appear on our pages.
Always ActiveNecessary cookies help make a website usable by enabling basic functions like page navigation and access to secure areas of the website. The website cannot function properly without these cookies.
| Name | Domain | Purpose | Expiry | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| wpl_user_preference | www.creative-chemistry.org.uk | WP GDPR Cookie Consent Preferences. | 1 year | HTTP |
| JSESSIONID | ichemlabs.cloud.chemdoodle.com | A generic technical cookie used for storing user session identifier in web applications. | 55 years | HTTP |
Marketing cookies are used to track visitors across websites. The intention is to display ads that are relevant and engaging for the individual user and thereby more valuable for publishers and third party advertisers.
Analytics cookies help website owners to understand how visitors interact with websites by collecting and reporting information anonymously.
PreferencesPreference cookies enable a website to remember information that changes the way the website behaves or looks, like your preferred language or the region that you are in.
UnclassifiedUnclassified cookies are cookies that we are in the process of classifying, together with the providers of individual cookies.